The reaction of hydrazinium sulfate and chlorosulfonic acid in pyridine leads to the pyridinium salt of the hydrazine disulfonate anion, [(SO₃)HNNH(SO₃)]²⁻. The salt is the starting material for the preparation of further hydrazine disulfonates, for example of alkaline metals and barium. In all compounds, the [(SO₃)HNNH(SO₃)]²⁻ anion adopts the gauche conformation. The conformer is chiral but all of the investigated compounds crystallize as racemates. The disulfonate anion can occur in another constitution with the two sulfonate groups attached to only one nitrogen atom. This so-called hydrazine iso-disulfonate, [H₂NN(SO₃)₂]²⁻, has been prepared through a substitution reaction between potassium imidodisulfonate, K[HN(SO₃)₂], and hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid, H₂NOSO₃H. The hydrazine iso-disulfonate anion has been crystallized as potassium and barium compounds, respectively. The compounds were characterized by XRD, vibrational spectroscopy, DFT calculations, and thermal analyses.
N₂H₄ Derived Sulfonic Acids: Hydrazine Disulfonate, [(SO₃)HNNH(SO₃)]²⁻, and Hydrazine Iso-disulfonate, [H₂NN(SO₃)₂]²⁻
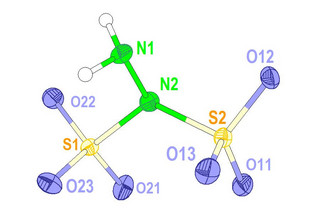
The hydrazine iso–disulfonate anion, [H₂NN(SO₃)₂]²⁻ of the structure K₂[H₂NN(SO₃)₂].